day5休息~
哈希表理论基础
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%A1%A8%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
⭐什么时候想到用哈希法,当我们遇到了要快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里的时候,就要考虑哈希法。 这句话很重要,大家在做哈希表题目都要思考这句话。
LeetCode242 有效的字母异位词
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解: https://programmercarl.com/0242.%E6%9C%89%E6%95%88%E7%9A%84%E5%AD%97%E6%AF%8D%E5%BC%82%E4%BD%8D%E8%AF%8D.html
哈希表是根据关键码的值而直接进行访问的数据结构。其实数组就是一张哈希表。
思路:定一个record数组记录字符串s里字符出现的次数,数组大小为26就可以了,初始化为0,因为字符a到字符z的ASCII也是26个连续的数值。
python中ord()函数返回字符ASCII数值
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
record = [0] * 26
for i in s:
record[ord(i) - ord('a')] += 1
for i in t:
record[ord(i) - ord('a')] -= 1
for i in range(26):
if record[i] != 0:
#record数组如果有的元素不为零0,说明字符串s和t 一定是谁多了字符或者谁少了字符
return False
return True
⭐python还能用defaultdict和Counter解题
LeetCode349 两个数组的交集
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0349.%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E7%9A%84%E4%BA%A4%E9%9B%86.html
直接用了python中的set:
class Solution(object):
def intersection(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
set1 = set(nums1)
set2 = set(nums2)
res = set1 & set2 # 交集
return list(res)
还有一种方法是用了字典和集合:
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
# 使用哈希表存储一个数组中的所有元素
table = {}
for num in nums1:
table[num] = table.get(num, 0) + 1
# 使用集合存储结果
res = set()
for num in nums2:
if num in table:
res.add(num)
del table[num]
return list(res)
LeetCode202 快乐数
题目链接/文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0202.%E5%BF%AB%E4%B9%90%E6%95%B0.html
-
难点1:取数值各个位上的单数操作
-
python
divmod()函数把除数和余数运算结果结合起来,返回一个包含商和余数的元组(a // b, a % b)。 -
def get_sum(self,n: int) -> int: new_num = 0 while n: n, r = divmod(n, 10) new_num += r ** 2 # 乘方 return new_num -
或者:
-
n_str = str(n) for i in n_str: new_num+=int(i)**2
-
-
难点2:题目中说了会 无限循环,那么也就是说求和的过程中,sum会重复出现,当我们遇到了要快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里的时候,就要考虑哈希法了。所以这道题目使用哈希法,来判断这个sum是否重复出现,如果重复了就是return false, 否则一直找到sum为1为止。
- 无限循环的例子:

- 无限循环的例子:
class Solution(object):
def isHappy(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
record = set()
while True:
newsum = self.get_sum(n)
if newsum == 1:
return True
elif newsum in record:
return False
else:
record.add(newsum)
n = newsum
def get_sum(self,n):
newsum = 0
while(n):
n, r = divmod(n, 10)
newsum += r ** 2
return newsum
LeetCode1 两数之和
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0001.%E4%B8%A4%E6%95%B0%E4%B9%8B%E5%92%8C.html
⭐用map解决
⭐什么时候使用哈希法,当我们需要查询一个元素是否出现过,或者一个元素是否在集合里的时候,就要第一时间想到哈希法。
⭐需要一个集合来存放我们遍历过的元素,然后在遍历数组的时候去询问这个集合,某元素是否遍历过,也就是 是否出现在这个集合。
⭐本题不仅要知道元素有没有遍历过,还要知道这个元素对应的下标,需要使用 key-value结构来存放,key来存元素,value来存下标,那么使用map正合适。
再来看一下使用数组和set来做哈希法的局限。
- 数组的大小是受限制的,而且如果元素很少,而哈希值太大会造成内存空间的浪费。
- set是一个集合,里面放的元素只能是一个key,而两数之和这道题目,不仅要判断y是否存在而且还要记录y的下标位置,因为要返回x 和 y的下标。所以set 也不能用。
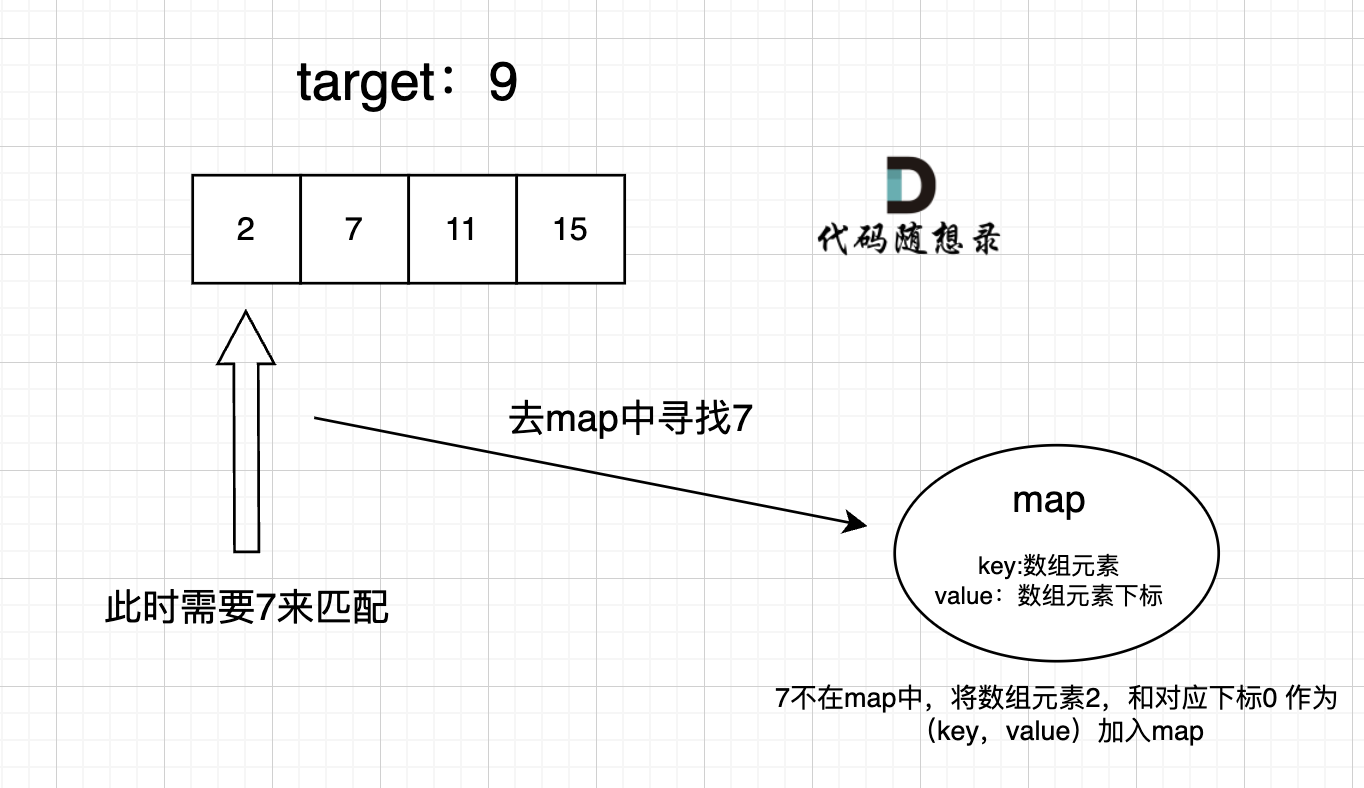
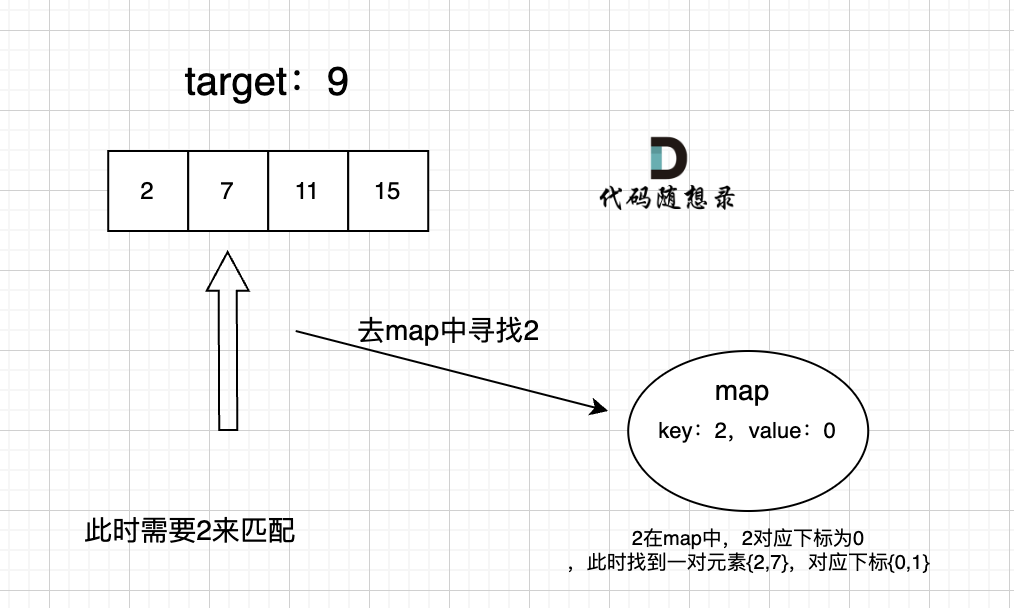
此时就要选择另一种数据结构:map ,map是一种key value的存储结构,可以用key保存数值,用value再保存数值所在的下标,即map中的存储结构为 {key:数据元素,value:数组元素对应的下标}。
在遍历数组的时候,只需要向map去查询是否有和目前遍历元素匹配的数值,如果有,就找到的匹配对,如果没有,就把目前遍历的元素放进map中,因为map存放的就是我们访问过的元素。
过程如下:
⭐enumerate()函数用于将一个可遍历的数据对象(如列表、元组或字符串)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标,一般用在 for 循环当中。
>>> seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']
>>> list(enumerate(seasons))
[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]
>>> list(enumerate(seasons, start=1)) # 下标从 1 开始
[(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')]
⭐python字典的用法:https://www.runoob.com/python/python-dictionary.html
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
record = dict()
for index, num in enumerate(nums):
need_num = target - num
# 遍历当前dict,并在map中寻找是否有匹配的key
if need_num in record:
return [record[need_num], index]
else: # 加入dict
record[num] = index